What is a phishing email?
Phishing emails are created to look similar to ones sent from legitimate companies, in the hopes of tricking unsuspecting people to give away their personally identifiable information (PII). Naturally, the criminals are usually targeting financial information, such as credit card numbers or bank logins.
PII includes sensitive personal information, such as financial and medical records, SSN, biometric info, and more.
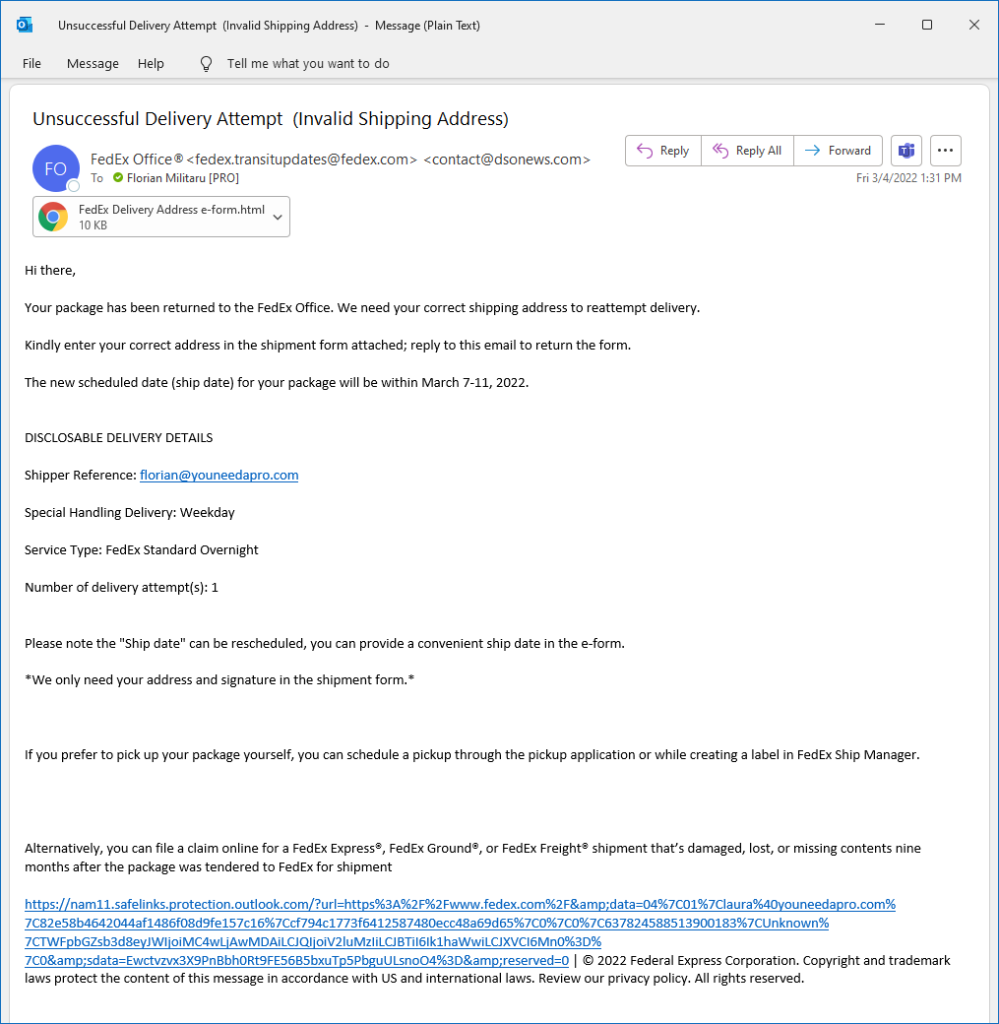
Let’s take a FedEx ‘Unsuccessful Delivery Attempt’ email as an example and dissect it:
Grammar mistakes
One of the first issues with many phishing emails are the glaring typos and grammar mistakes, which this email doesn’t have.
The mistakes don’t mean the criminal doesn’t know how to use a spell checker, in fact, it’s by design. Making obvious errors just removes the alert (potential) victims from the pool, and only includes the people who may be in a hurry or who just don’t pay enough attention, making them an easier target to scam.
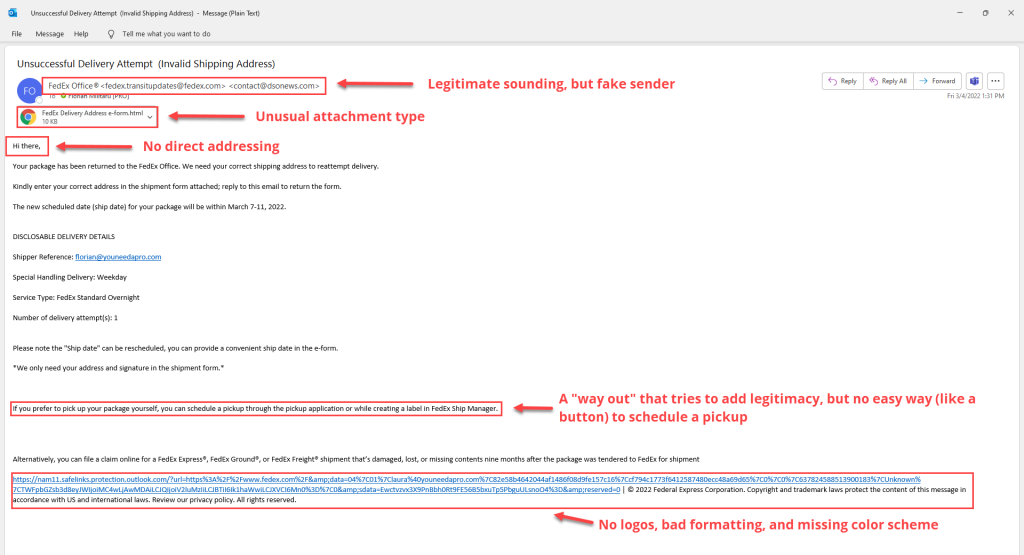
Invalid sender address

When checking who sent the email, always make sure to check the sender email. In this case, the scammer has added the legitimate-sounding email to the Display Name of their email account (usually it would be first name + last name) to make it look like the email is coming from a real sender.
Upon closer investigation, you can see that the sender is co*****@*****ws.com, which sounds like a huge 🚩🚩🚩
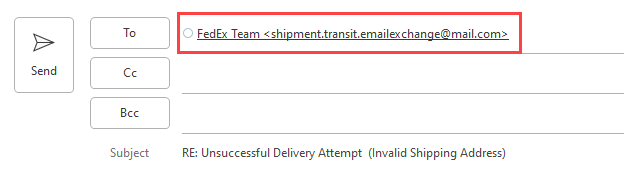
Even further, when I hit Reply (which the scammer requested I do after filling out their form), the recipient email is sh****************************@**il.com. Definitely not FedEx.
Missing addressing
Most professional emails (unless cold emails, which can be legitimate) address the recipient by their first/last name.
When an email is supposedly sent to you from a business you have worked with before, but they refer to you as ‘Sir/Madam’, or it just starts with ‘Hi there’ or ‘Hello’, it should add a point to the warning bells in your head.
In this email, it’s clear the scammer doesn’t know anything about me except for the email address, which is the only piece of information they emphasize.
Attempts at legitimizing the email
Scammers often try to legitimize the email by adding a ‘way out’. In this case, the way out is mentioned at the end of the email:

Unfamiliar or unexpected attachment(s)
With an unsuccessful delivery email, you would expect a button in the email body that takes you to the FedEx home page and lets you reschedule. In this case, there is an HTML attachment included in the email, which you are supposed to open and insert your information.
HTML files can run malicious code on your computer to allow scammers access to your computer and data
Although sometimes you might receive a legitimate HTML attachment, it is fairly unlikely and you should always exercise caution with these types of attachments. Even if you don’t type in your information in the file that opened, scammers might still be able to access your personal information, so be particularly careful with opening any attachment.
Bad formatting
Usually, scam emails don’t look too similar to legitimate emails. In this case, you can’t find a single FedEx logo, their signature purple hue has not been used, and the email looks poorly formatted.
Little details like that add another warning sign that should make you think it is a fake email. You might notice there is a long link at the bottom of the email — in the original, the whole link is ‘www.fedex.com’, which is another attempt in trying to legitimize the email.
Since we have Outlook Advanced Security set up, all links are being checked for malware to ensure my device and data won’t be compromised.
- Verify the sender email and domain
- Don’t click on any unusual attachments
- Check for personal addressing
- Check for bad/unprofessional formatting
- Look out for signs of poor legitimization attempts


