RAID is an abbreviation from Redundant Array of Independent Disks.
Having independent disks is the main idea behind RAID since it improves the fault tolerance and the chances that if something goes wrong, you will not lose your important data.
Fun fact: it was called Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks at first, but since the vendors thought it suggests the low price of the disks, it was later changed to Redundant Array of Independent Disks.
In a nutshell, RAID distributes your data between several hard (or solid-state) drives, resulting (depending on the chosen RAID level) in more fault-tolerance or speed. You can use RAID on your personal computer, but they are used primarily for servers.
Now that we got that out of the way let’s explain the most popular levels without getting too technical.
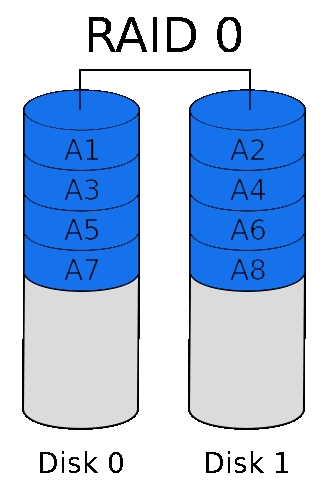
RAID 0, also called DISK STRIPING
Imagine you have two hard drives. You want to write data on them as fast as you can. What do you do? You could write data on both drives at the same time. For example, if you want to write the word “Hello” on your disks, you would write “H,” “l” and “o” to drive number 1, and “e,” “l” to the second drive.
Since you can perform two actions at once, the writing times are cut in half. The negative side of RAID 0 is that if one of the drives fails or there’s a power outage, you lose all your data.
RAID 0 is recommended for services that need to be exceptionally fast. Such services might include live streaming services or video editing, which might otherwise take a long time.
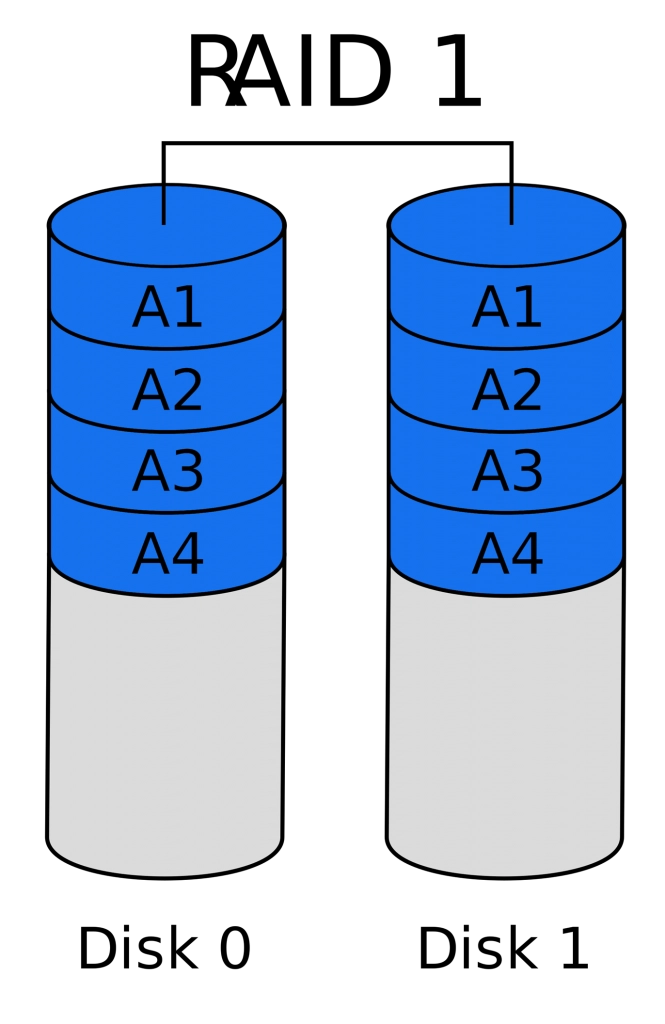
RAID 1, also called DISK MIRRORING
If you have valuable information that you can’t afford to lose (but you still have a limited budget), RAID 1 might be the right solution.
Mirroring doubles the same data on two (or more) drives, making it more fault-tolerant, but slower. It’s like writing with both hands at the same time – it’s going to slow the system down since it doubles all the actions, but when one drive fails, you can always turn to the other to ask for your valuables back.
Another downside is that it uses more space, so it is more expensive than just having one drive.
RAID 1 is recommended for services that store critical information, such as application servers or drives that have essential data.
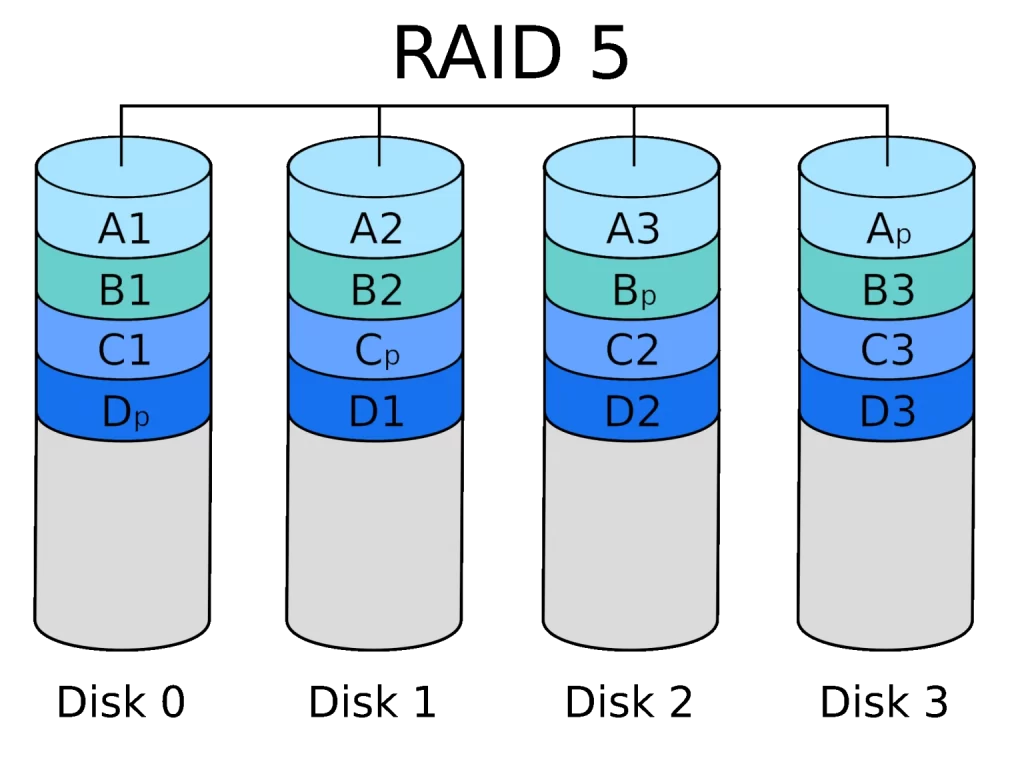
RAID 5, also called DISK STRIPING WITH PARITY
RAID 5 is a slightly more complicated version of RAID 0.
All the data gets written on (at least) 3 disks, but the third disk contains the sum (parity) of data written on the first two disks. For example, if the sum of the first disk’s data is 10, the sum of the second one is 20, then the parity number is 10 + 20 = 30.
If the primary disk fails, the parity can be used for what it’s meant for – the second drive’s sum gets subtracted from the parity (30 – 20 = 10).
With that calculated number, the missing data can be rewritten.
RAID 5 is faster than just disk mirroring (RAID 1) and offers more fault tolerance. However, it is not as fast as RAID 0, since the drives still need to calculate the parity after each write. It is also quite expensive since it requires at least three drives, and 1/3 of the storage space is taken up by the parity.
RAID 5 is recommended for file storage servers, business servers, and NAS devices.
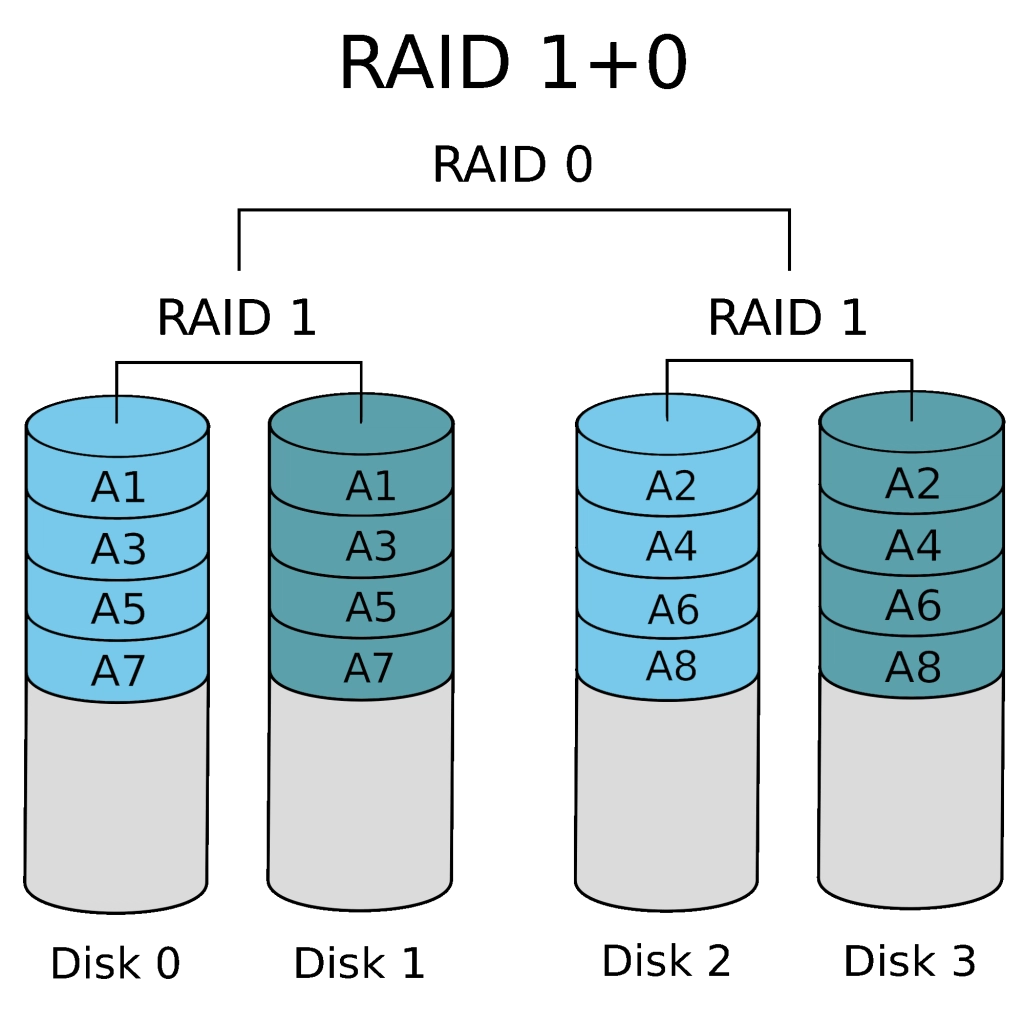
RAID 1+0, also called DISK STRIPING + MIRRORING
This RAID does what it says – it combines the first and second RAID levels.
In short, it combines the speed of RAID 0 and the performance of RAID 1. The main downside of using RAID 1+0 is that it is expensive since you need at least four drives.
Also, writing times are twice as slow as the read times, since two copies will be written simultaneously.
RAID 1+0 is recommended for servers that must do a lot of writing.
Conclusion
Even if you use RAID, you should still have a good data backup. Especially if you’re a small business, keeping your data safe and sound is crucial.
Disasters tend to strike when you least expect them, and it is always good to be prepared ahead of time.
Protek-IT offers data backup for small businesses that is both reliable and cost-effective.



