Phishing has always been a threat, but now, with the rise of AI, it’s even more dangerous — phishing 2.0 is here. It’s smarter, more convincing, and harder to detect. Understanding this new threat is important for businesses and individuals alike, especially those in Chicago and beyond who rely on managed services providers (MSPs) to keep their data secure.
A recent study found a staggering 60% increase in AI-driven phishing attacks. This is a wake-up call: phishing is only getting worse. Let’s see how AI amplifies phishing and what you can do to protect yourself.
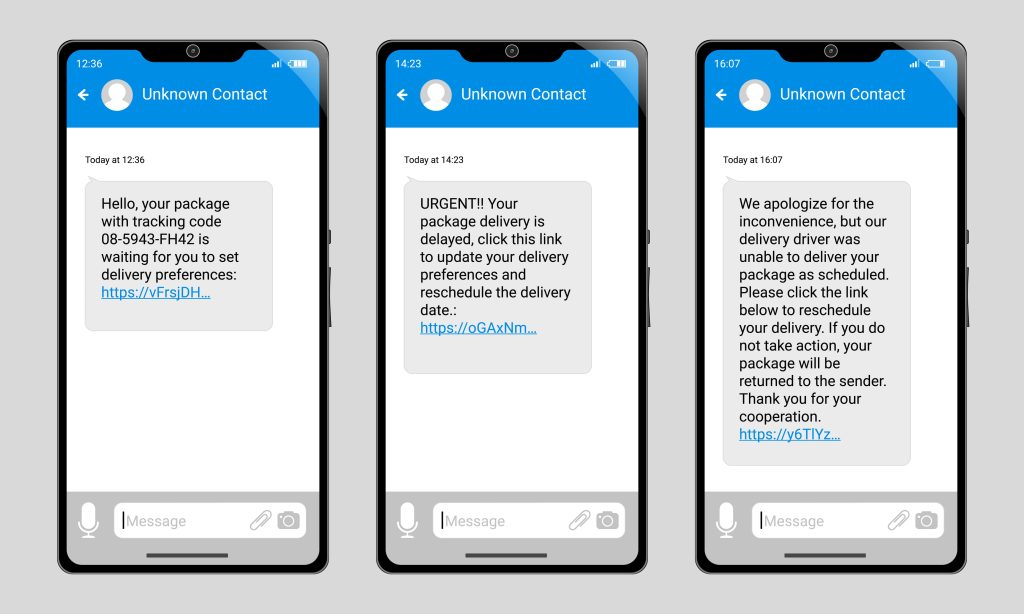
The Evolution of Phishing
Phishing began quite simply. Attackers would send out mass emails, hoping someone would take the bait. These emails were often crude, filled with poor grammar and obvious lies. Most people could spot them easily.
But times have changed, and attackers now leverage AI to refine their tactics. AI helps them quickly craft more convincing messages and target specific individuals, making phishing more effective and harder to detect.
How AI Enhances Phishing
Creating Realistic Messages
AI can analyze vast amounts of data, studying how people (in your industry) write and speak. This allows it to create realistic phishing messages that mimic the tone and style of legitimate communications. These messages can sound like they come from a real person, making them much harder to spot.
Personalized Attacks & Spear Phishing
AI gathers information from social media and other sources to create highly personalized messages. These messages might reference your job, hobbies, or recent activities, increasing the chances that you’ll believe the message is real. In Chicago, where business networking is vibrant, such targeted attacks can be particularly effective.
Spear phishing is more sophisticated than regular phishing and targets specific individuals or organizations. AI makes spear phishing even more dangerous by helping attackers conduct in-depth research on their targets, letting them craft highly tailored messages that are hard to distinguish from legitimate ones.
Automated Phishing
AI automates many aspects of phishing. It can send out thousands of phishing messages quickly and adapt them based on responses. If someone clicks a link but doesn’t enter information, AI can send a follow-up email. This persistence increases the likelihood of success.
Deepfake Technology
Deepfakes use AI to create realistic fake videos and audio. Attackers can leverage deepfakes in phishing attacks, such as creating a video of a CEO asking for sensitive information. This adds a new layer of deception, making phishing even more convincing.
The Impact of AI-Enhanced Phishing
- Increased Success Rates:
AI makes phishing more effective, leading to more data breaches. Companies lose money, and individuals face identity theft and other issues. In a business hub like Chicago, the impact can be significant.
- Harder to Detect:
Traditional phishing detection methods struggle against AI-enhanced attacks. Spam filters may not catch them, and employees may not recognize them as threats. This makes it easier for attackers to succeed.
- Greater Damage:
AI-enhanced phishing can cause more damage. Personalized attacks can lead to significant data breaches, allowing attackers to access sensitive information and disrupt operations. The consequences can be severe.
How to Protect Yourself
- Be Skeptical:
Always be skeptical of unsolicited messages, even if they appear to come from a trusted source. Verify the sender’s identity and don’t click on links or download attachments from unknown sources.
- Check for Red Flags:
Look for red flags in emails, such as generic greetings, urgent language, or requests for sensitive information. Be cautious if the email seems too good to be true.
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication:
MFA adds an extra layer of security. Even if an attacker gets your password, they’ll need another form of verification, making it harder for them to access your accounts.
- Educate Yourself and Others:
Education is key. Learn about phishing tactics and stay informed about the latest threats. Share this knowledge with others, especially within your organization. Training can help people recognize and avoid phishing attacks.
- Verify Requests for Sensitive Information:
Never provide sensitive information via email. If you receive a request, verify it through a separate communication channel. Contact the person directly using a known phone number or email address.
- Use Advanced Security Tools:
Invest in advanced security tools. Anti-phishing software can help detect and block phishing attempts. Email filters can screen out suspicious messages. Keep your security software up to date and ask for your MSP for more info.
- Report Phishing Attempts:
Report phishing attempts to your IT team or email provider. This helps them improve their security measures and protect others from similar attacks.
- Enable Email Authentication Protocols:
Email authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC help protect against email spoofing. Ensure these protocols are enabled for your domain to add an extra layer of security to your emails. Ask for your IT Support company for help if you’re unsure where to begin.
- Regular Security Audits:
Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities in your systems. Addressing these vulnerabilities can prevent phishing attacks and enhance your overall cybersecurity posture.
Need Help protecting your business against Phishing 2.0?
AI-backed phishing is a serious threat. These attacks are more convincing and harder to detect. Have you had an email security review lately? Maybe it’s time.
Contact us today to schedule a chat about phishing safety and how our managed services can help protect your business from these sophisticated threats. We’re here to ensure your cybersecurity is robust and reliable in Chicago and beyond.



